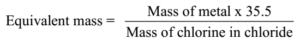Science > Chemistry > Concept of Atomic Mass and Equivalent Mass > Oxide Formation, Reduction, and Chloride Formation Method
In the last article, we have studied the hydrogen displacement method to find the equivalent mass of an element. In this article, we shall study three more methods oxide formation method, reduction method, and chloride formation method.
The equivalent mass of a substance is the number of parts by mass of the substance which combines with or displaces or contains 1.008 parts by mass of hydrogen, 8 part by mass of oxygen, or 35.5 part by mass of chlorine. If the equivalent mass is expressed in grams then it is called gram equivalent mass (GEM).
Illustration:
1.008 parts by weight of Hydrogen combines with 35.5 parts by weight of chlorine to give 36.5 parts by weight of HCI. Thus the equivalent mass of chlorine is 35.5.
Method – II (Oxide Formation Method):
Procedure:
A known mass of an element is reacted with oxygen. Mass of the oxide formed is measured. The mass of oxygen in the oxide is calculated using formula
Mass of oxygen = Mass of the oxide – Mass of the element
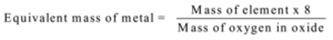
Numerical Problems on Oxide Formation Method:
Example – 01:
0.4 g of metal, when heated in air, gave 0.72 g of the metal oxide. Find the equivalent mass of the metal.
Given: Mass of metal = 0.4 g, Mass of oxide = 0.72 g
Solution:
Mass of oxygen = 0.72 – 0.4 = 0.32 g
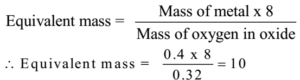
Ans: The equivalent mass of the metal is 10.
Example – 02:
If the mass of the copper taken is 0.324 g and mass of the product on heating its nitrate is 0.406 g. calculate the chemical equivalent of copper.
Given: Mass of metal = 0.324 g, Mass of oxide = 0.406 g,
Solution:
Mass of oxygen = 0.406 – 0.324 = 0.082 g

Ans: Hence chemical equivalent of the metal is 31.61.
Example – 03:
1.08 g of metal oxide on heating decomposes to give pure metal and 56.0 ml of oxygen at NTP. What is the chemical equivalent of metal?
Given: Mass of metal oxide = 1.08 g, Volume of oxygen at NTP = 56.0 ml = 0.056 dm3.
Solution:
One mole of any gas occupies 22.4 dm3 by volume at NTP.

Mass of metal = Mass of oxide – Mass of oxygen = 1.08 – 0.08 = 1 g

Ans: The chemical equivalent of the metal is 100.
Example – 04:
0.139 g of metal, when dissolved in dilute hydrochloric acid, evolved 29.5 ml of hydrogen when collected over water at 13 °C and 741 mm pressure. What would be the mass of the oxygen present in 100 g of the oxide of the metal if the aqueous tension at 13 °C is 11.2 mm?
Given: W = 0.139 g, V = 29.5 ml, P = 741 mm of Hg, f = 11.2 mm of Hg, T = 13 °C = 13 + 273 = 286 K, PO = 760 mm of Hg, TO = 273 K.
Solution:

Let ‘x’ g be the mass of oxygen in the oxide
Mass of oxide = 100 g, Mass of oxygen = x g
∴ Mass of metal = (100 – x) g

∴ 57.6 x = 800 – 8x
∴ 65.6 x = 800
∴ x = 800/ 65.6 = 12.20 g
Ans: 100 g of metal contains 12.20 g of oxygen
Method – III (Reduction Method):
Procedure:
A known mass of a metal oxide is reduced to metal. Mass of the metal obtained is measured. The mass of oxygen in the oxide is calculated using formula
Mass of oxygen = Mass of oxide – Mass of element
The equivalent mass is calculated using the formula

Numerical Problems on Reduction Method:
Example – 01:
1.44 g of the metal oxide on reduction gave 0.8 g of metal. Find the equivalent mass of the metal.
Given: Mass of metal = 0.8 g, Mass of oxide = 1.44 g, Mass of oxygen = 1.44 – 0..8 = 0.64 g
Solution:

Ans: The equivalent mass of the metal is 10.
Example – 02:
On heating 0.8567 g of copper oxide in a current of hydrogen, the resulted in the formation of 0.6842 g of copper. Find the atomic mass of copper.
Given: Mass of copper = 0.6842 g, Mass of oxide = 0.8567 g
Solution:
Mass of oxygen = 0.8567 – 0.6842 = 0.1725 g

Ans: The equivalent mass of the metal is 31.63.
Method – IV (Equivalent Mass by Chloride Formation Method):
Procedure:
A known mass of a metal is reacted with chlorine. Mass of the chloride obtained is measured. The mass of chlorine in the chloride is calculated using formula
Mass of chlorine = Mass of chloride – Mass of the element
The equivalent mass is calculated using the formula

Example – 01:
2.00 g of metal yielded 2.656 g of its chloride. Find the equivalent mass of the metal.
Given: Mass of metal = 2.00 g, Mass of chloride = 2.656 g
Solution:
Mass of chlorine = 2.656 – 2.00 = 0.656 g

Ans: The equivalent mass of the metal is 108.2.
Example – 02:
The chloride of a metal contained 52.85 % of metal. What is the equivalent mass of the metal?
Given: % of metal = 52.85,
Solution:
% of Chlorine = 100 – 52.85 = 47.15, Consider 100 g of chloride
Mass of metal = 52.85 g, Mass of chloride = 47.15 g

Ans: The equivalent mass of the metal is 39.79.
In the next article, we shall study double displacement method and metal displacement method to determine equivalent mass of a substance.
Previous Topic: Equivalent Mass by Hydrogen Displacement Method
Next Topic: Equivalent Mass by Double Displacement Method