Science > Chemistry > Physical Chemistry > Ionic Equilibria > Ionic Product of water
In this article, we shall study concepts of the ionic product of water, pH and pOH of a solution and their importance.
Ion Equilibrium in Water:
Water has electrical conductivity, hence it must undergo dissociation. “Dissociation of pure water to a very little extent into H+ and OH– ions by itself is called as self ionisation of water. Water is a very weak electrolyte. In water, an equilibrium between ions and unionised water molecule exists as,
H2O ⇌ H+ + OH–
H+ + H2O ⇌ H3O+
The net reaction is
H2O + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + OH–
H3O+ is called the hydronium ion
Applying law of mass action to above equilibrium, we have
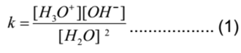
Now water is a very weak electrolyte. It dissociates in a very small amount. Hence practically the concentration of unionised water is almost the same as starting concentration. Hence [H2O] = constant. Similarly Practically [H3O+] = [H+]. Therefore the equation (1) becomes.
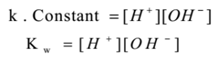
This relation is known as the ionic product of water.
The product of the molar concentration of H+ and OH- ions pure water or an aqueous solution at constant temperature is constant which is called the ionic product of water.
At 298 K, for pure water [H+] = [OH–] = 1 x 10-7 mole dm-3
Thus Kw = [H+] [OH–] = (1 x 10-7) x (1 x 10-7) = 1 x 10-14
Thus at 298 K ionic product of water is 1 x 10-14
- When small amount of acid is added to water, the concentration of H+ ions increases and that of OH– ions decrease. i.e. [H+] > [OH–] i.e. [H+] > 1 x 10-7
- When an alkali is added to water then OH– ion concentration becomes higher than that of H+ ions. i.e. [OH–] > [H+] i.e. [OH–]. > 1 x 10-7
- In neutral solution. H+ and OH– ion concentration are equal. i.e. [H+] = [OH–] = 1 x 10-7 mole dm-3
- Thus concept of ionic products of water helps us in classifying aqueous solutions as acidic, basic and neutral.
pH and pOH of a solution:
pH of a solution:
The negative logarithm to the base 10 of molar concentration of H+ ions in a solution is called as pH of a solution.
Mathematically, pH = – log10[H+]
For pure water or a neutral solution.at 298 K.
[H+] = 1 x 10-7 moles/dm3
∴ pH = – log10(1 x 10-7) = – (-7) log1010 = + 7 (1) = 7
pOH of a Solution:
The negative logarithm to the base 10 of molar concentration of OH– ions in a solution is called as pOH of a solution.
Mathematically, pOH = – log10[OH–]
For pure water or a neutral solution.at 298 K.
[OH–] = 1 x 10-7 moles/dm3
∴ pOH = – log10(1 x 10-7) = – (-7) log1010 = + 7 (1) = 7
Relation Between pH and pOH:
Ionic product of water is given by Kw = [H+] [OH–]
For pure water or an aqueous solution, Kw = 1 x 10-14 at 298 K
∴ [H+] [OH–] = 1 x 10-14
Taking logs of both sides of the equation to the base 10
log10[H+] + log10[OH–] = log10(1 x 10-14)
∴ log10[H+] + log10[OH–] = -14 log1010
∴ log10[H+] + log10[OH–] = -14(1) = -14
Multiplying both sides of the equation by -1
∴ – log10[H+] – log10[OH–] = 14
But pH = – log10[H+] and pOH = – log10[OH–]
∴ pH + pOH = 14
Thus the sum of pH and pOH for pure water or any aqueous solution is equal to 14.
pH Scale or Sorensen’s Scale:
Scientist Sorensen in 1909 introduced a convenient scale to express hydrogen ion (H+) concentration to decide acidic, alkaline or neutral nature of the solution , is known as pH scale. The negative logarithm to the base 10 of the molar concentration of H+ ions in a solution is called as pH of a solution. The pH scale expresses all degrees of acidity or alkalinity of a dilute aqueous solution.
As the concentration of acid decreases the pH value increases from 0 to7.while as the concentration of base decreases the pH value decreases from 14 to7. For pure water or aqueous neutral solution, pH = 7.
It is to be noted that pH scale is used for a dilute aqueous solution only i.e. their molarity is less than 1 M.
Two acids monobasic and diabasic have the same pH. Does this mean that the molar concentration of the two acids is identical?
A monobasic acid
dissociates as
HA ⇌
H+ + A–
Thus 1 mole of monobasic acid gives 1 mole of H+ ions.
A dibasic acid dissociates as
H2A ⇌ 2H+ + A–
Thus 1 mole of dibasic acid gives 2 moles of H+ ions.
Hence if the pH of the two solutions is equal, the molar concentration of monobasic acid will be twice the molar concentration of dibasic acid.
One reply on “Ionic Product of water”
clear, jargon-free explanation, thank you so much