Science > Chemistry > Physical Chemistry > Ionic Equilibria > Ostwald’s Dilution Law
In this article, we shall study the Ostwald’s dilution law and its application to weak electrolytes, like weak acids and weak bases.
Ostwald’s Dilution Law:
A mathematical expression of the law of mass actions that gives the relationship between equilibrium constant/dissociation constant, the degree of dissociation and concentration at constant temperature is called Ostwald’s dilution law.
Statement:
The degree of ionization (or dissociation) of any weak electrolyte is inversely proportional to the square root of concentration and directly proportional to the square root of dilution.
Explanation:
If α is the degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte, C is its concentration and V is the dilution. Then
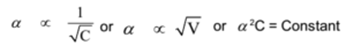
Ostwald’s dilution law is not applicable to strong electrolytes since their dissociation reaction is irreversible.
Ostwald’s Dilution Law for Weak Electrolyte:
Let one mole of a binary weak electrolyte BA be dissolved in water and the solution is made ‘V’ dm3 by volume. Let ‘α’ be the degree of dissociation of the electrolyte at equilibrium. Weak electrolyte dissociates as
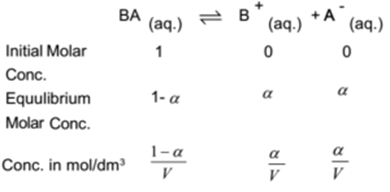
By applying the law of mass action to above equilibrium,
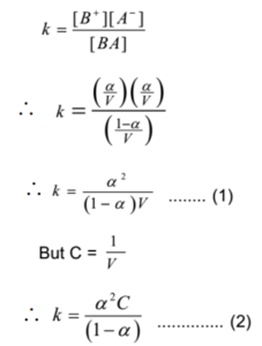
The expressions (1) and (2) are known as Ostwald’s dilution law. Where K = equilibrium constant.
For weak electrolyte α is very small, hence 1 – α = 1

Thus, the degree of ionization (or dissociation) of any weak electrolyte is inversely proportional to the square root of concentration and directly proportional to the square root of dilution. This relation is known as Ostwald’s law.
Expression for Dissociation Constant of Weak Acid:
Let one mole of a binary weak acid HA be dissolved in water and the solution is made ‘V’ dm3 by volume. Let ‘α’ be the degree of dissociation of the acid at equilibrium.
Weak acid dissociate in an aqueous solution and equilibrium exists as,


Where Ka = dissociation constant for the acid
Depending upon the values of C, the degree of dissociation varies in order to keep the value of Ka constant. This is known as Ostwald’s dilution law.
For weak acid α is very small, hence 1 – α = 1

This is the expression for dissociation constant of a weak acid.

Concentration of H+ ions is given by

Expression for Dissociation Constant of Weak Base:
Let one mole of a weak base BOH be dissolved in water and the solution is made ‘v’ dm3 by volume. Let ‘a’ be the degree of dissociation of the base at equilibrium. Weak base dissociate in an aqueous solution and equilibrium exists as,


Where Kb = Ionisation constant or dissociation constant of base
Depending upon the values of C, the degree of dissociation varies in order to keep the value of Kb constant. This is known as the dilution law.
For weak base α is very small, hence 1 – α = 1

This is the expression for dissociation constant of a weak base.

Concentration of OH– ions is given by

One reply on “Ostwald’s Dilution Law”
Wow nice very useful website