Science > Chemistry > Chemical Kinetics > Rate of Zero Order Reaction
In this article, we shall study the analytical treatment to the zero-order reaction, and the rate of zero-order reaction.
Order of Reaction:
The overall order of the reaction is defined as the sum of the exponents to which the concentration terms in the rate law are raised.
Let us consider a general reaction
aA + bB → Products
The rate law can be written as
Rate = K [A]x [B]y …………… (1)
Thus the overall order of the reaction is (x + y).
Zero Order Reaction:
Integrated Law for Zero-Order Reaction:
A reaction whose rate is independent of the concentration of reactants is called a zero-order reaction.
Let us consider a general reaction

Let [A]o be initial concentration of A (i.e at t = 0) and be final concentration of A (i.e at t = t)
Integrating both sides of above equation
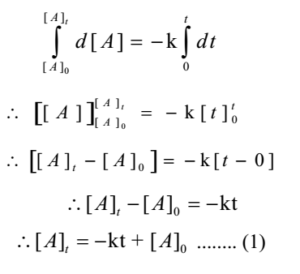
This relation is known as integrated law for zero-order reaction.
Expression for the Integrated Rate Constant:
From equation (1) we have
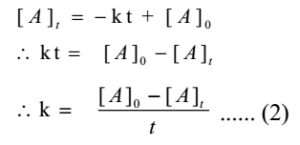
This is an expression of the integrated rate constant for the zero-order reaction.
Unit of Integrated Rate Constant:
The unit of integrated rate constant is mol dm-3 t-1 ( mol dm-3 s-1 or mol dm-3 min-1, mol dm-3hr-1)
Half-Life of Zero Order Reaction:
The half-life of a reaction is defined as the time required for the reactant concentration to fall to one half of its initial value. Thus for t = t1/2, [A]t = ½[A]o
The integrated rate constant for the zero-order reaction is given by

This is an expression of the half-life of a zero-order reaction.
Graphical Representation of Zero Order Reaction in Different Ways:
The graph of rate of reaction against time:
The differential rate law for the zero-order reaction is


Thus the graph of the rate of reaction versus time is a straight line parallel to the time axis.
The graph of Rate of reaction against Initial Concentration:
The differential rate law for the zero-order reaction is

Thus the rate is independent of the concentration of reactants. Hence Thus the graph of the rate of reaction versus concentration of reactants is a straight line parallel to concentration axis.

The graph of Concentration of the reactants against time:

The differential rate law for the zero order reaction is
[A]t = – kt + [A]o
It is of the form y = mx + c. Thus the graph of concentration at instant versus time is a straight line with y-intercept. [A]o. The slope of the straight line is – k.
Examples of Zero-order Reaction
- Decomposition of NH3 on a hot platinum surface:

- Decomposition of Nitrous oxide in presence of platinum as a catalyst:
