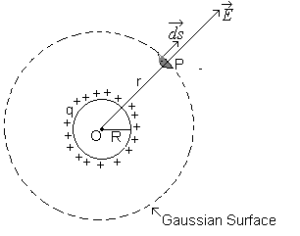
Science > Physics > Electrostatics > Electric Intensity Due to Charged Sphere
In this article, we shall study to solve problems to find electric intensity at a point due to a charged sphere.
Example – 01:
A charge of 0.002 µC is given to an isolated conducting sphere of radius 0.5 m. Calculate the electric intensity (i) at a point on the surface of the sphere and (ii) at a point 1.5 m away from its centre. (iii) at the centre of the sphere.
Given: Charge = 0.002 µC = 0.002 x 10-6 C = 2 x 10-9 C, radius of sphere = R = 0.5 m, k = 1, εo = 8.85 x 10-12 C2/Nm2
To Find: Electric intensity (i) at a point on the surface of the sphere and (ii) at a point r = 1.5 m
Solution:
Surface charge density is given by
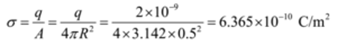
Electric intensity on the surface of a charged sphere is given by
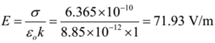
Electric intensity at a point outside charged sphere is given by

Electric intensity at any point inside a charged conductor is zero. Hence electric intensity at the centre of the sphere is zero.
Ans: Electric intensity at a point on the surface of the sphere is 71.93 V/m, Electric intensity at a point at a distance of 1.5 m from centre of the charged sphere is 7.992 V/m and electric intensity at the centre of the sphere is zero.
Example – 02:
An isolated conducting sphere of radius 0.1 m placed in vacuum carries a positive charge of 0.l µC. Find the electric intensity at a point at a distance of 0.2 m from the centre.
Given: Charge = 0.1 µC = 0.1 x 10-6 C = 1 x 10-7 C, radius of sphere = R = 0.1 m, distance of point from centre = r = 0.2 m, k = 1, εo = 8.85 x 10-12 C2/Nm2
To Find: Electric intensity at a point r = 0.2 m =?
Solution:
Surface charge density is given by

Electric intensity at appoint outside the charged sphere is given by

Ans: Electric intensity at a point at a distance of 0.2 m from the centre of the charged sphere is 2.248 x 104 V/m
Example – 03:
The electric intensity at a point at a distance of 1 m from the centre of a sphere of radius 25 cm is 104 N/C. Find the surface density of charge on the surface of the sphere; The sphere is situated in air.
Given: Radius of sphere = R = 25 cm = 0.25 m, distance of point from centre = r = 1 m, k = 1, εo = 8.85 x 10-12 C2/Nm2, Electric intensity = E = 104 N/C
To Find: Surface charge density = σ =?
Solution:
Electric intensity at appoint outside charged sphere is given by

Ans: The surface charge density is 1.416 x 10-6 C/m2
Example – 04:
A metal sphere of radius 20 cm is charged with 12.57 µC situated in air. Find the surface density of charge. Calculate the distance of point from centre of sphere where electric intensity is 1.13 x 105 N/C
Given: Radius of sphere = R = 20 cm = 0.20 m, Charge = 12.57 µC = 12.57 x 10-6 C, k = 1, εo = 8.85 x 10-12 C2/Nm2, Electric intensity = E = 1.13 x 105 N/C
To Find: Surface charge density = σ = ?, distance of point from centre = r =?
Solution:
Surface charge density is given by

Electric intensity at appoint outside the charged sphere is given by

Ans: Surface charge density = σ = 2.5 x 10-5 C/m2 and the distance of the point from the centre of the sphere where the electric intensity is 1.13 x 105 N/C is 1 m
Example – 05:
A metal sphere of radius 1 cm is charged with 3.14 µC. Find the electric intensity at a point situated at a distance of 1 m from centre of metal sphere.
Given: Charge = 3.14 µC = 3.14 x 10-6 C, radius of sphere = R = 1 cm = 0.01 m, k = 1, εo = 8.85 x 10-12 C2/Nm2
To Find: Electric intensity at a point r = 1 m
Solution:
Surface charge density is given by

Electric intensity at appoint outside charged sphere is given by

Ans: Electric intensity at a point 1 m from centre of the charged sphere is 2.825 x 104 N/C
Example – 06:
A uniformly charged metal sphere of radius 1.2 m has a surface charge density of 16 µC/m2. Find the charge on the sphere. What is the electric flux emanating from the sphere?
Given: Surface charge density = 16 µC/m2= 16 x 10-6 C/m2, radius of sphere = R = 1.2 m, k = 1, εo = 8.85 x 10-12 C2/Nm2
To Find: Charge on sphere = q = ?, electric intensity flux = ϕ = ?
Solution:
Surface charge density is given by

Electric flux is given by

Ans: Charge on the sphere is 290 µC and electric flux is 3.277 x 107 Nm2/C
Example – 07:
A metal sphere of diameter 20 cm is charged with 4π µC. Find the surface density of charge on the sphere and the distance of a point from the centre of the sphere where the electric intensity is 2.26 x 105 V/C.
Given: Diameter of sphere = 20 cm, radius of sphere = R = 20/2 = 10 cm = 0.10 m, Charge = 4π µC = 4π x 10-6 C, k = 1, εo = 8.85 x 10-12 C2/Nm2, Electric intensity = E = 2.26 x 105 N/C
To Find: distance of point from centre = r =?
Solution:
Surface charge density is given by

Electric intensity at a point outside charged sphere is given by

Ans: Surface charge density = σ = 10-4 C/m2 and the distance of the point from the centre of the sphere where the electric intensity is 2.26 x 105 N/C is 7.07 m
Example – 08:
The electric flux due to a point charge q passing through a sphere of radius 15 cm is 12 x 103 Nm2/C. What would be the flux due to the charge through a sphere of radius 18 cm? Find q.
Given: Radius of sphere = R = 15 cm = 0.15 m, Electric flux = ϕ = 12 x 103 Nm2/C, k = 1, εo = 8.85 x 10-12 C2/Nm2
To Find: Electric flux when radius of sphere is 18 cm and charge = q =?
Solution:
The charge on the surface of sphere behaves like it is concentrated at the centre of the sphere. Hence the electric flux is independent of the radius of the sphere. Hence I case of a sphere of radius 18 cm, the electric flux will remain the same. 12 x 103 Nm2/C.

Ans: the flux due to the charge through a sphere of radius 18 cm is also 12 x 103 Nm2/C, and charge on the sphere is 1.062 x 10-7 C
Example – 09:
A point charge is enclosed by spherical Gaussian surface of radius 5 cm. If electrical flux passing through it is 5 x 103 Nm2/C. Find the charge and flux density over the surface of the sphere.
Given: Radius of sphere = R = 5 cm = 0.05 m, Electric flux = ϕ = 5 x 103 Nm2/C, k = 1, εo = 8.85 x 10-12 C2/Nm2
To Find: charge = q =?, flux density over the surface of sphere = ?
Solution:
Electric flux is given by

Surface charge density is given by

Electric flux density over the surface of a sphere is given by

Ans: The charge is 1.408 x 10-8 C and flux density on the surface of the sphere is 1.591 x 105 N/C.
Example – 10:
A hollow metal ball 10 cm in diameter is given a charge of 0.01 C. What is the intensity of the electric field at a point 20 cm from the centre of the ball.
Given: Charge = 0.01 C, radius of sphere = R = 10 cm = 0.1 m, k = 1, εo = 8.85 x 10-12 C2/Nm2
To Find: Electric intensity at a point r = 20 cm = 0.2 m
Solution:
Surface charge density is given by

Electric intensity at a point outside charged sphere is given by

Ans: Electric intensity at a point at a distance of 0.2 m from centre of cthe harged sphere is 2.248 x 109 N/C
Previous Topic: Gauss’s Theorem and its Applications
Next Topic: Mechanical Force Per Unit Area of Charged Conductor