Science > Physics > Communication > Modulation Before the concept of the modulation, the signal used to be sent in form continuous wave with periodic interruption as in morse code. To code, send and decode such message high expertise was required. The direct current is not suitable for transmitting the data because of its steady nature. […]
Categories
Modulation
- Post author By Hemant More
- Post date November 16, 2019
- No Comments on Modulation
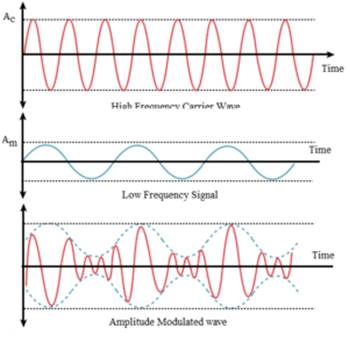
- Tags Aerial, Amplitude modulation, Antenna, Carrier waves, Continuous wave, Frequency modulation, Modulation, Need of modulation, Operating range, Phase modulation, Power radiated by antenna, Pulse, Pulse amplitude modulation, Pulse duration modulation, Pulse position modulation, Sinusoidal wave, Size of antenna, Transmitter, Wireless communication


