Science > Physics > Magnetism > Numerical Problems on Current-Carrying Solenoid In this article, we shall study problems on current-carrying solenoid and current-carrying coil suspended in a uniform magnetic field. Example – 01: A solenoid has a core of material of relative permeability 4000. The number of turns is 1000 per metre. A current of […]
Tag: Magnetic field
Science > Physics > Magnetism > Numerical Problems on Magnetic Susceptibility In this article, we shall study problems to calculate magnetization, magnetic susceptibility, magnetic permeability, etc. μ = B / H μr = B / B0 Example – 01: Find the magnetization of the bar magnet of length 10 cm and cross-sectional area 3 cm2. […]
Magnetization and Magnetic Intensity
Science > Physics > Magnetism > Magnetization and Magnetic Intensity In this article, we shall study the origin of magnetism, magnetic intensity, magnetization, and magnetic susceptibility. Magnetic Field Due to Current-Carrying Coil: The magnetic induction at a point on the axis at a distance of ‘x’ from the centre of a circular coil of radius […]
Science > Physics > Magnetism > Magnetic Induction and Magnetic Potential at any Point In this article, we shall study to derive an expression for magnetic induction and magnetic potential at any point in a magnetic field created by a bar magnet. Magnetic Induction at Any Point Due to a Short Bar Magnet: Consider a […]
Science > Physics > Magnetic Effect of Electric Current >Numerical Problems on Toroids or Rowland Ring Example 01: A Rowland ring (toroid) of ferromagnetic material of a mean radius 15 cm has 3000 turns of wire wound it. The relative permeability of the material is 1000. What is the magnetic field in a core when […]
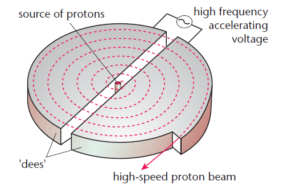
Science > Physics > Magnetic Effect of Electric Current > Cyclotron The device which uses the electric or magnetic field to guide and accelerate a beam of charged particles to high speed is called a particle accelerator. Charged particles used may be protons or electrons. These high-velocity particles are used in nuclear physics and high […]
Tangent Galvanometer

Science > Physics > Magnetic Effect of Electric Current > Tangent Galvanometer In this article, we shall study, the principle, construction, working, sensitivity, and accuracy of the tangent galvanometer. Principle: The tangent galvanometer works on the principle of tangent law. The magnetic needle is subjected to two magnetic fields which are perpendicular to each other. […]
Ammeter and Voltmeter
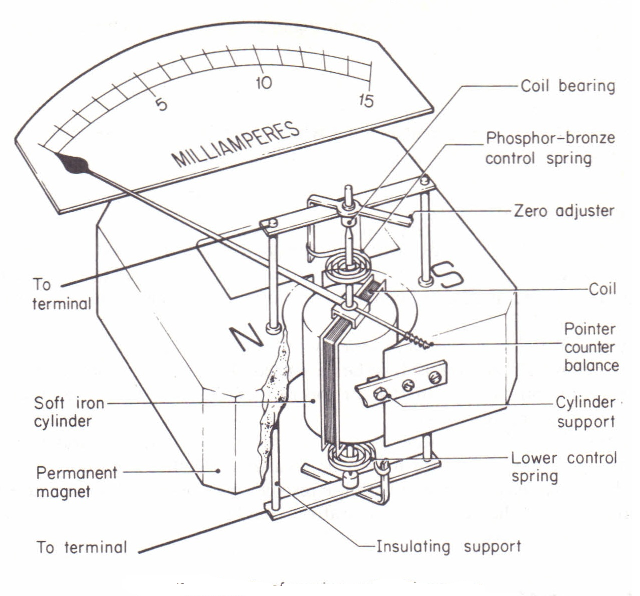
Science > Physics > Magnetic Effect of Electric Current > Ammeter and Voltmeter Ammeter: An ammeter is an electrical measurement device (apparatus) which is used to measure the electric current in the electrical circuit. Requirements of Good Ammeter: The resistance of an ammeter must be as small as possible. The ideal resistance of an ammeter […]
Moving Coil Galvanometer

Science > Physics > Magnetic Effect of Electric Current > Moving Coil Galvanometer In this article, we shall study principle, construction, working, sensitivity and accuracy of the moving coil galvanometer Principle: When a current-carrying coil is suspended in a uniform magnetic field it is acted upon by a torque. Under the action of this torque, […]
Ampere’s law

Science > Physics > Magnetic Effect of Electric Current > Ampere’s law In this article, we shall study the Ampere’s law and its application in finding magnetic induction due to long straight conductor, solenoid and toroid. Statement: The line integral of the magnetic field B around any closed path is equal to μ0 times the net […]