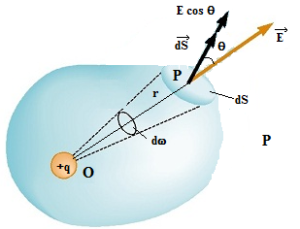
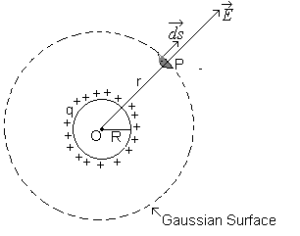
Science > Physics > Electrostatics > Normal Electric Induction In this article, we shall study the concept of normal electric induction, electric field, and electric flux. Normal Electrical Induction: The number of tubes of induction passing normally through a unit area in an electric field is called Normal electric induction. Total Normal Electrical Induction: The […]
Categories
Normal Electric Induction
- Post author By Hemant More
- Post date February 7, 2020
- No Comments on Normal Electric Induction
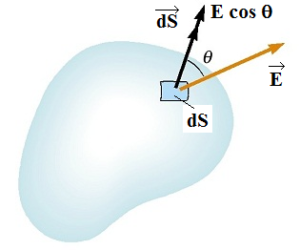
- Tags Attractive force, Coulomb, Coulomb's law, Dielectric constant of medium, Electric dipole, Electric dipole moment, Electric field, Electric field intensity, Electric flux, Electric induction, Electric intensity, Electric potential, Electron volt, Electrostatics, Gravitational force, Lines of force, Lines of induction, Nature of force, Non-uniform electric field, Normal electric induction, Potential difference, Principle of superposition of forces, Radial electric field, Repulsive force, Static electricity, Total normal electric induction, Tubes of force, Tubes of induction, Uniform electric field, Unit of charge