Amino acids contain an amino (–NH2) and carboxyl (–COOH) functional groups. The amino acids in proteins are called alpha (α)-amino acids because the amino group is attached to the α-carbon. A carbon directly connected to carbonyl carbon is termed α-carbon. Depending upon the relative position of the amino group with respect to the carboxyl group, the amino acids can be […]
Category: Biology
Unicellular organisms are capable of having an independent existence and of performing the essential functions (metabolic activities) of life. Anything less than a complete structure of a cell does not ensure independent living. Hence, the cell is the fundamental structural and functional unit of all living organisms. All the living organisms, from the smallest (unicellular) to the […]
Epithelium or Epithelial Tissue
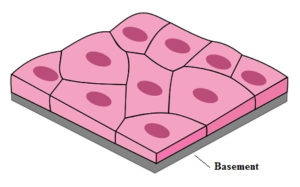
Science > Biology > Zoology > Histology > Epithelium or Epithelial Tissue In this article, we shall study about the epithelium or epithelial tissue. Higher-level organisms have multicellular structure. The cells differ from one another in their shape, size. Cells arise from pre-existing cells by the process of cell division. In multicellular organisms, cells are […]
Criteria for Animal Classification
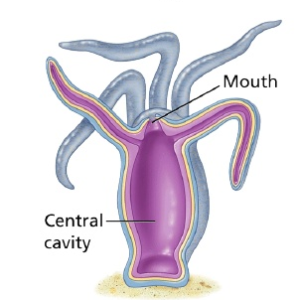
Science > Biology > Zoology > Criteria for Animal Classification In this article, we shall study the criteria for animal classification. Animals are classified as follows: On the Basis of Number of Germ Layers: Animals in which the cells are arranged in two embryonic layers, an external ectoderm, and an internal endoderm, are called diploblastic […]
Types of Endosperm and Fruit Formation

Science > Biology > Botany > Reproduction in Plants > Types of Endosperm and Fruit Formation In the last article, we have studied fertilization and the formation of the endosperm. In this article, we shall study types of the endosperm. Types of endosperm Nuclear Endosperm: The primary endosperm nucleus divides repeatedly to form a large […]
Fertilization

Science > Biology > Botany > Reproduction in Plants > Fertilization In last article, we have studied about pollination and its types. In this article, we shall study the process of fertilization. Out Breeding Devices: Most angiosperms produce bisexual flowers (hermaphrodite). But most of them avoid self-pollination naturally or we can say that in plants […]
Pollination and its Types

Science > Biology > Botany > Reproduction in Plants > Pollination and its Types In this article, we are going to study important step in sexual reproduction in plants i.e. pollination. We shall also study its types. Transfer of pollen grains (shed from the anther) to the stigma of a pistil is termed pollination. Depending […]
Androecium and Gynoecium

Science > Biology > Botany > Reproduction in Plants > Androecium and Gynoecium The flower is the reproductive unit in the angiosperms. It is meant for sexual reproduction. A typical flower has four different kinds of whorls arranged successively on the stalk or pedicel, called thalamus or receptacle. These whorls are calyx, corolla, androecium and […]
Sexual Reproduction in Plants

Science > Biology > Botany > Reproduction in Plants > Sexual Reproduction in Plants Sexual reproduction is also called amphimixis (Gk. amphi – both, mixis – union) or syngenesis (Gk. syn – together, genesis – origin) or amphigony (Gk. amphi – both, gony – marriage). In this article, we shall study sexual reproduction in plants. […]
Asexual Reproduction in Plants

Science > Biology > Botany > Reproduction in Plants > Asexual Reproduction in Plants In this article, we shall study asexual reproduction in plants. Reproduction: Reproduction is defined as a biological process in which an organism gives rise to young ones (offspring) similar to itself. The offspring grow, mature and in turn produce new offspring. […]