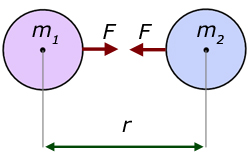
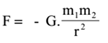Science > Physics > Gravitation > Numerical Problems on Newton’s Law of Gravitation In this article, we shall learn numerical problems to calculate the gravitational force of attraction between two bodies. Example – 01: Calculate the gravitational force of attraction between two metal spheres each of mass 90 kg, if the distance between their centres […]