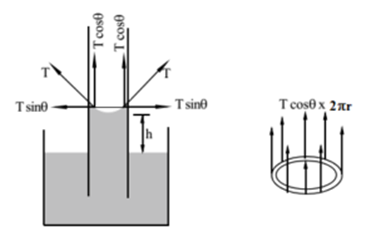
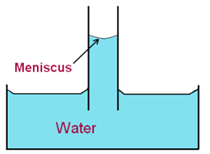
Science > Physics > Surface Tension > Numerical Problems on Capillary Action In this article, we shall study to solve problems on capillary action. Important Formulae: and Jurin’s law, hr = constant where h = height of liquid level in the capillary T = Surface tension ρ = Density of liquid r = Radius of […]
Categories
Numerical Problems on Capillary Action
- Post author By Hemant More
- Post date November 21, 2019
- 6 Comments on Numerical Problems on Capillary Action
- Tags Adhesion, Adhesive force, Angle of contact, Capillarity, Capillary, Capillary action, Capillary tube, Cohesion, Cohesive force, Concave meniscus, Convex meniscus, Liquid drop, Range of molecular attraction, Soap bubble, Sphere of molecular influence, Spherical membrane, Surface Energy, Surface tension