Researches by J.J. Thomson, Dalton, Rutherford, and Mosley showed that an atom is the smallest but not the ultimate particle of the matter. An atom consists of subatomic particles, protons, neutrons, and electrons called fundamental particles. Besides these, particles like mesons, positrons, neutrinos are also associated with the atomic structure. In this article, we shall study, the basic terminology of nuclear chemistry.
Terms Used in Nuclear Chemistry:
Now let us study certain basic terms used in nuclear chemistry.
Atomic number (Z):
The number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom or the number of electrons present in an atom is called the atomic number. It is denoted by the letter ‘Z’.
Example: In a Sodium atom there are 11 protons. Hence the atomic number of Sodium is 11
Characteristics of Atomic Number:
- It is the total number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom.
- Atoms of the same element have the same atomic number.
- Isotopes have the same atomic number.
- Chemical properties of elements are periodic properties of its atomic number.
Neutron number (N):
The number of neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom is known as the neutron number. It is denoted by ‘N’
Mass number (A):
The total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom of the element is called mass number. The mass number is denoted as ‘A’.
A = Z + N or N = A – Z
Example: In a Sodium atom, the total number of protons and neutrons is 23. Hence the mass number of Sodium is 23.
Characteristics of Mass Number:
- It is the total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom.
- Atoms of the same element can have different mass numbers.
- Isobars have the same mass number
- Chemical properties of elements are not periodic properties of its mass number.
Representation of Atom in Symbolic Form:
Generally, every atom X is represented as
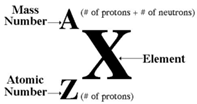
Distinguishing Between Mass Number and Atomic Number:
| Mass Number | Atomic Number |
| It is total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom. | It is the total number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom. |
| Atoms of same element can have different mass numbers. | Atoms of the same element have same atomic number. |
| Isobars have the same mass number | Isotopes have same atomic number |
| Chemical properties of elements are not periodic properties of its mass number. | Chemical properties of elements are periodic properties of its atomic number. |
| In Sodium atom total number of protons and neutrons is 23. Hence mass number of Sodium is 23. | In Sodium atom there are 11 protons. Hence atomic number of Sodium is 11 |
Isotopes:
Different atoms of the same element having the same atomic number but having different mass numbers are known as isotopes.
Examples :
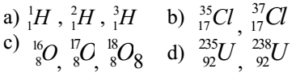
Characteristics of Isotopes:
- Different Atoms of the same element having the same atomic number but having different mass numbers are known as isotopes.
- Isotopes are the atoms of the same element.
- They have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
- They have the same number of protons but the different number of neutrons.
- Since they have the same atomic number they show the same chemical properties.
- They occupy the same positions in the periodic table.
Isobars:
Atoms of the different elements having a different atomic number but having same mass numbers are known as isobars.
Examples :
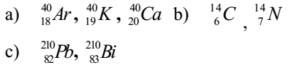
Characteristics of Isobars:
- Atoms of the different elements having different atomic numbers but having the same mass numbers are known as isobars.
- Isobars are the atoms of different elements.
- They have the same mass number but different atomic numbers.
- They have a different number of protons and neutrons.
- Since they have a different atomic number they show different chemical properties.
- They occupy different positions in the periodic table.
Isotones:
Atoms of the different elements having the different atomic number, different mass number but having same neutron number are known as isotones.
Examples:

Characteristics of Isotones:
- Atoms of the different elements having different atomic numbers, different mass numbers but having the same neutron number are known as isotones.
- Isotones are the atoms of different elements.
- They have different mass numbers and different atomic numbers.
- They have the same number of neutrons.
- Since they have a different atomic number they show different chemical properties.
- They occupy different positions in the periodic table.
Distinguishing Between Isotopes and Isobars:
| Isotopes | Isobars |
| Different Atoms of the same element having same atomic number but having different mass numbers are known as isotopes. | Atoms of the different elements having different atomic number but having same mass numbers are known as isobars. |
| Isotopes are the atoms of same element. | Isobars are the atoms of different elements. |
| They have same atomic number but different mass numbers. | They have same mass number but different atomic numbers. |
| They have same number of protons but different number of neutrons. | They have different number of protons and neutrons. |
| Since they have same atomic number they show same chemical properties. | Since they have different atomic number they show different chemical properties. |
| They occupy same positions in periodic table. | They occupy different positions in periodic table. |
| 1H1(Hydrogen), 1H2(Deuterium (D) ), 1H3 (Tritium ( T )) | 18Ar40, 19K40 and 20Ca40 |