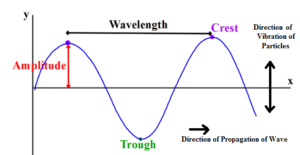
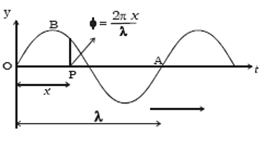
Science > Physics > Wave Motion > Numerical Problems on Simple Harmonic Progressive Wave Example – 01: The equation of transverse simple harmonic progressive wave is y = 3 sin 2π(t/0.04 – x/40), where the length is expressed in cm and the time in seconds. Calculate the wavelength, frequency, amplitude and the speed of the […]
Categories
Numerical Problems on Simple Harmonic Progressive Wave
- Post author By Hemant More
- Post date January 17, 2020
- 5 Comments on Numerical Problems on Simple Harmonic Progressive Wave
- Tags Amplitude of a wave, Condensation, Crest, Doubly periodic, Extension, Frequency of a wave, Longitudinal wave, One dimensional wave, Period of a wave, Periodic in space, Periodic in time, Rarefaction, Simple harmonic progressive wave, Three dimensional wave, Transverse wave, Trough, Two dimensional wave, Velocity of a wave, Wave, Wave Motion, Wave number, Wavelength, Wavelength of a wave