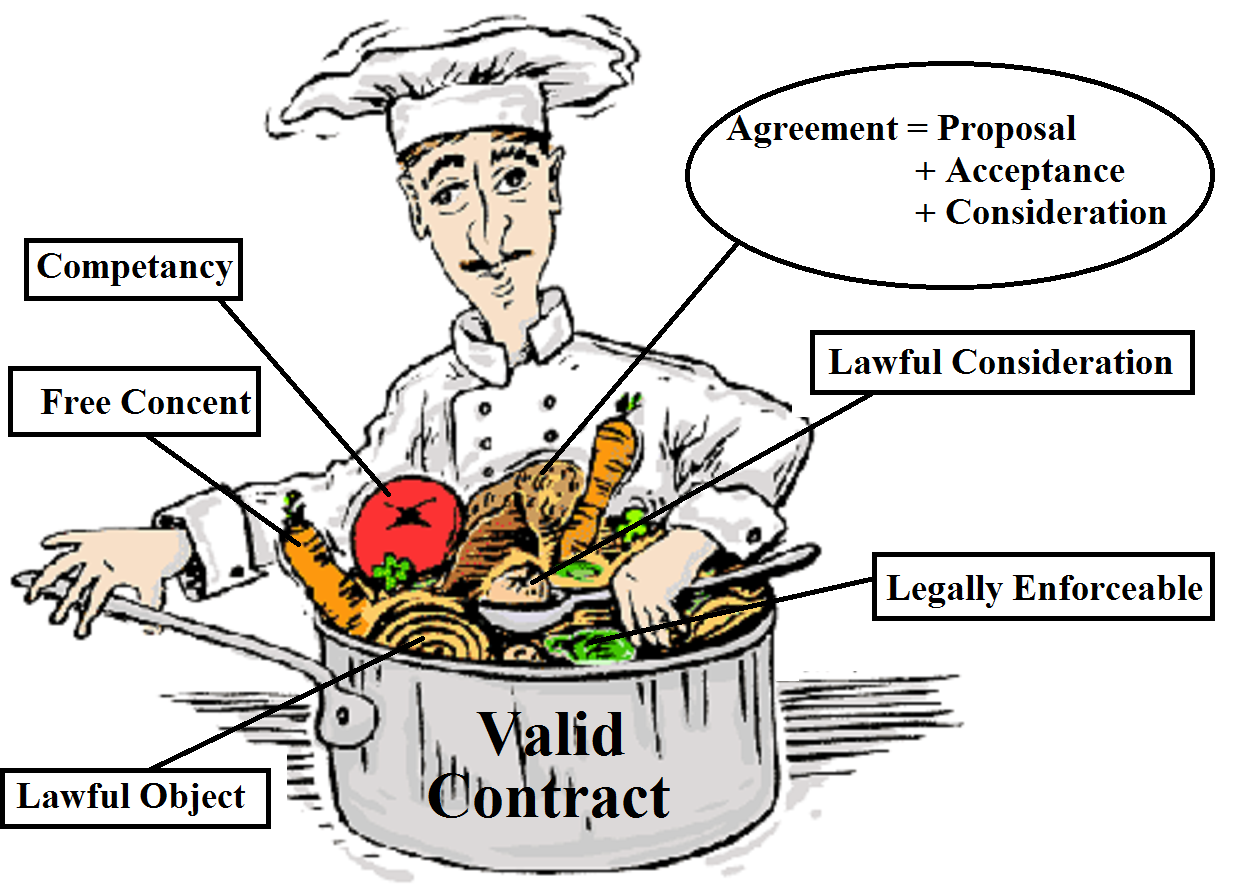
Law > Civil Laws > Indian Contract Act, 1872 > Proposal or Offer In contract proposal and acceptance of proposal are important ingredient. In this article, we shall discuss proposal in details. Section 2(h) of the Indian Contract Act , 1872, defines the term ‘Contract’ as “An agreement enforceable by law is a contract.” Section […]
Categories
Proposal or Offer
- Post author By Hemant More
- Post date March 4, 2019
- No Comments on Proposal or Offer
- Tags (1873) 29 LT 271, [1968] EWCA Civ 4, 1923(2) KB 261, 1942 1 All ER 220, 1952 2 QB 795, AIR 1987 SC 2354, AIR 2003 SC 858, Balfour v. Balfour, Balram Gupta v. Union of India, Bank of India v. O. P. Swaranakar, Communication of proposal, Express offer, Implied offer, Invitation to offer, Lalman Shukla v. Gauri Datt, Legal relation, n Jones v Padavatton, Offer, Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain v. Boots Cash Chemists (Southern) Ltd, Powell v. Lee, Proposal, Rose & Frank Co. v. Crompton & Bros. Ltd, Taylor v. Laird, Tinn v. Hoffman & Co., Uptron Rural District Council v. Powell, Weeks v. Tybaid