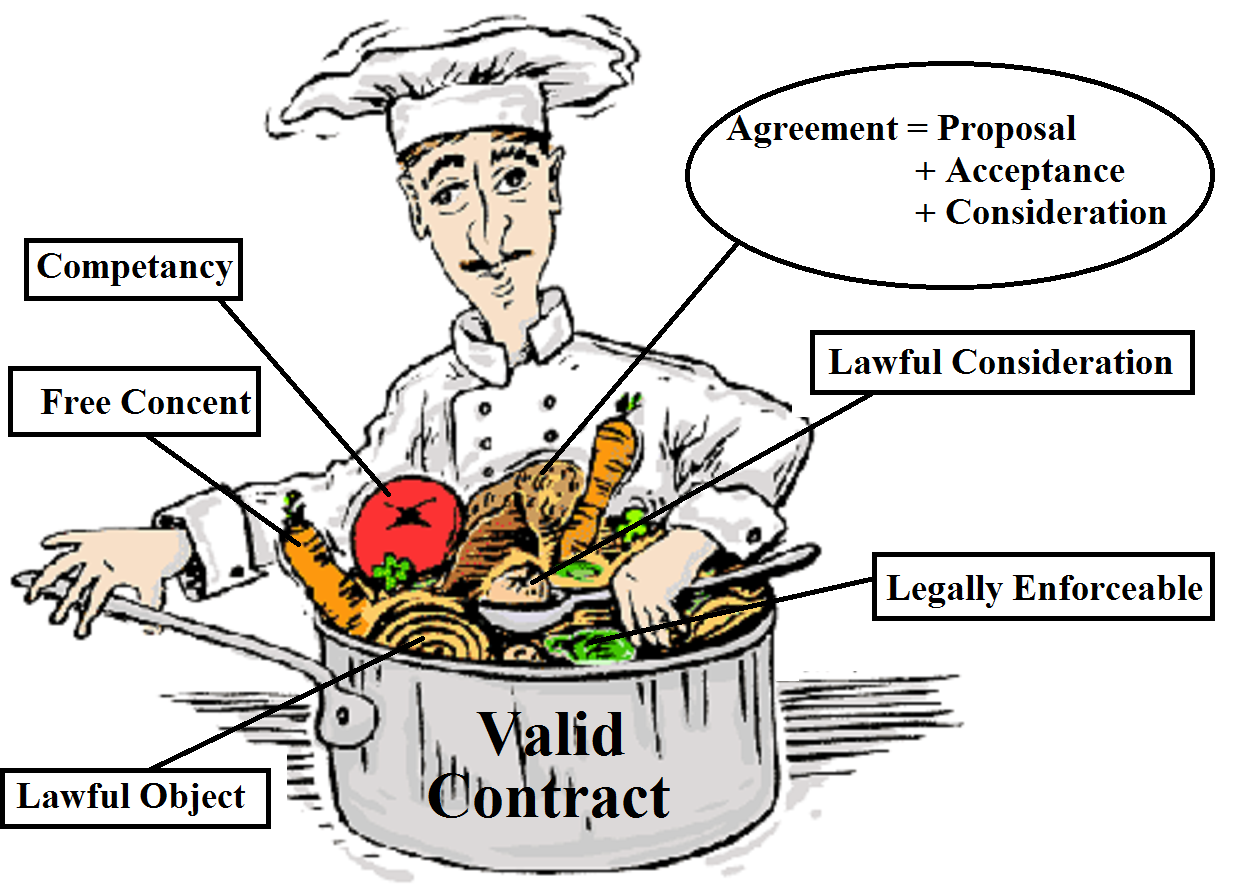
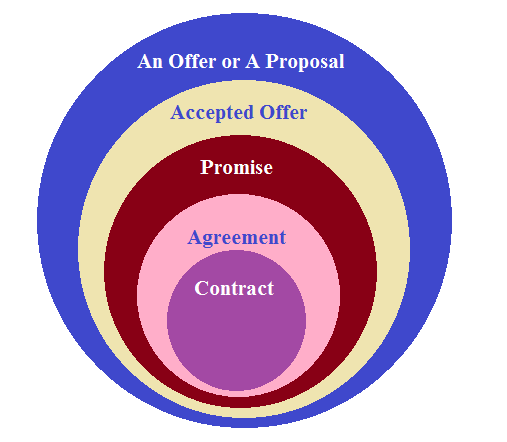
Indian Legal System > Civil Laws > Indian Contract Act, 1872 > Types of an Offer A proposal is main ingredient of a valid contract. The term “proposal” of the Indian Contract Act is synonymous to the term “Offer” in English law. Section 2(a)of the Indian Contract Act, 1872 defines proposal as “when one person […]
Categories
Types of an Offer
- Post author By Hemant More
- Post date March 4, 2019
- 3 Comments on Types of an Offer

- Tags (1918) 87 LJKB 677, (1840) 49 ER 132, (1857) 2H and N564, (1873) 29 LT 271, (1964) 3, 1942 1 All ER 220, Bangal Coal Co. Ltd. v. Homee Wadia & Co. (1899) L Bom. 97, Boulton v. Jones, Carlill v Carbolic Smoke Ball Co., Carlill v Carbolic Smoke Ball Co. 1893, Continuous offer, Counter offer, Cross offer, Express offer, General offer, Harvey v. Facey, Hyde v. Wrench, Implied offer, Open offer, Perclval Ltd. v. London County Council Asylums and Mental deficiency Committee, Philip & Co. v. Knoblanch, S.C.R. 774, Specific offer, Standing offer, Tinn v. Hoffman & Co., Union of India v. Madala Thathiah, Uptron Rural District Council v. Powell