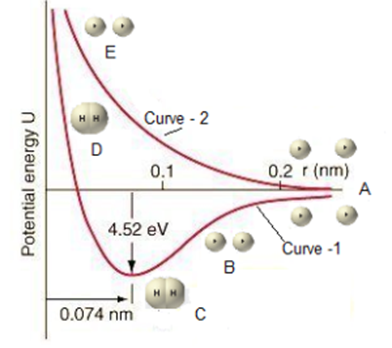
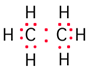
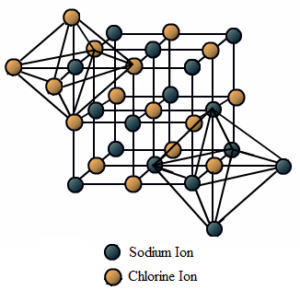
Science > Chemistry > Physical Chemistry > Nature of Chemical Bond > Valence Bond Theory Valence bond theory was proposed by Heitler and London in (1927) and it was extended by Pauling and Slater (1931). It is based on the following concepts. The pairing of electrons. Neutralization of opposite electron spins. Overlapping of orbitals containing […]
Valence Bond Theory