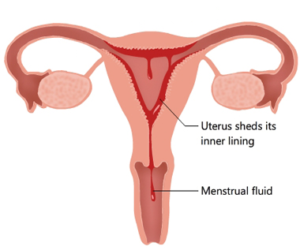
The menstrual cycle (Latin: mensis means a lunar month) is a characteristic of primates (monkeys, apes, and humans). Menstruation is defined as the cyclic discharge of blood carrying broken tissue materials through the vagina. In a human female, the fertility period extends from the age of puberty, i.e. about 11-13 years up to menopause, i.e. 45-50 years. The […]