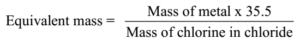Science > Chemistry > Concept of Atomic Mass and Equivalent Mass > Oxide Formation, Reduction, and Chloride Formation Method In the last article, we have studied the hydrogen displacement method to find the equivalent mass of an element. In this article, we shall study three more methods oxide formation method, reduction method, and chloride formation […]