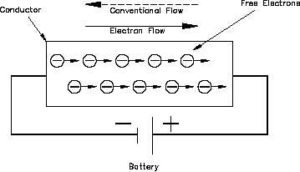
Science > Physics > Current Electricity > Introduction In this article, we shall study the concept of current electricity, the resistance, ohm’s law, and the conductance of a conductor. Electric Current Through Conductor: A conductor is made up of very minute particles called atoms. Atoms consist of a positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons […]
Introduction to Current Electricity