Science > Physics > Thermometry > Numerical Problems on Temperature Scales In the previous article, we studied measurement temperature, various scales to measure temperature viz: Celsius scale, Fahrenheit scale, and Kelvin scale, and also interconversion of temperature in different temperature scales. In this article, we shall study, the concept of specific heat and latent heat […]
Category: Physics
Concept of Temperature
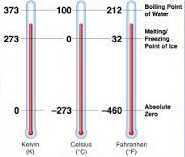
Science > Physics > Thermal Properties of Matter and Thermodynamics > Concept of Temperature In last article we have discussed concept of heat. In this article, we shall study the concept of temperature, different temperature scales, and convert temperature in different temperature scales. Defining Temperature: Temperature can be defined in several ways: It is measured […]
Discovery of Proton and Neutron
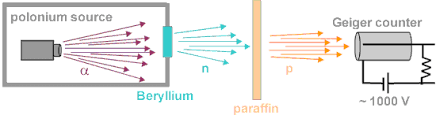
Science > Physics > Nuclear Physics > Discovery of Proton and Neutron Before the discovery of the atomic nucleus, there were ideas that all atoms are composed of hydrogen atoms (called by William Prout “protyles”). This hypothesis is known as Prout’s hypothesis. According to this hypothesis, the hydrogen atom was the only truly fundamental particles, […]
Nuclear Structure
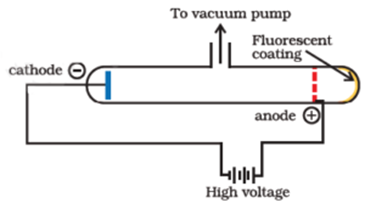
Science > Physics > Nuclear Physics > Nuclear Structure In this article, we shall discuss the composition of nucleus and concept of nuclear radius, nuclear vlume, and nuclear density. Geiger Marsden Experiment: A narrow beam of alpha particles from the radioactive source was incident on a thin gold foil. The scattering of alpha particles takes […]
Concept of Radioactive Decay

Science > Physics > Nuclear Physics > Concept of Radioactive Decay Transformation of radioactive element into another element (radioactive or non-radioactive) is known as radioactive decay or disintegration. In radioactive decay, the nucleus of a radioactive element called parent undergoes a spontaneous change accompanied by the emission of radiation and the formation of the nucleus […]
Electric Potential
Science > Physics > Electrostatics > Electric Potential Electric Potential at a Point: The electric potential at any point in the electric field is defined as the work that must be done by the external force to move unit positive charge from infinity to that point without acceleration. If W is the work done in […]
Photometry and Sources of Light
Science > Physics > Wave Theory of Light >Photometry and Sources of Light In this article, we shall study brief history of study of light, sources of light, andterminology of optics. History of Study of Light: Light is a form of that energy which simulates our vision. Around 400 B.C., it was proposed that particles […]
Introduction to Static Electricity

Science > Physics > Electrostatics > Introduction to Static Electricity Electricity is a very important form of energy which can be easily converted into other forms of energy. Electricity can be produced at one place and can be transmitted to long distances. Electricity is a branch of Physics which deals with charges, stationary and moving. […]
Correction to the Ideal Gas Equation

Science > Physics > Themodynamics > Correction to the Ideal Gas Equation In this article, we shall study the correction to ideal gas equation. Ideal Gas Equation: The equation of state for an ideal gas is given by PV = n RT Where, P = Pressure of gas, V = Volume of gas, n = No. of […]
Change of Phase

Science > Physics > Themodynamics > Change of Phase In this article, we should study the concept of phase, change of phase anfd the triple point of water. Phase: The phase of a substance is defined as its form which is homogeneous, physically distinct and mechanically separable from other forms of the substance. The term […]