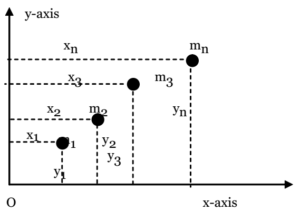
Science > Physics > Force > Centre of Mass and Centre of Gravity In this article. we shall study the concept of centre of mass and centre of gravity of a body and methods to locate them. Concept of Centre of Mass: The entire mass of a body is supposed to be concentrated at a […]
Centre of Mass and Centre of Gravity