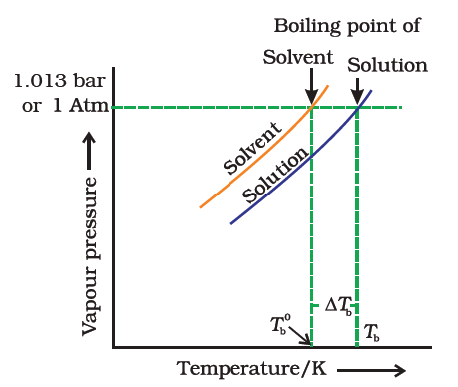
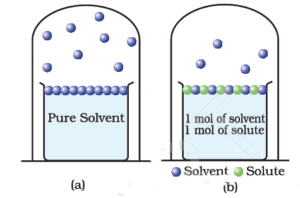
Science > Chemistry > Solutions and Their Colligative Properties > Boiling Point Elevation and Freezing Point Depression In this article, we shall study two colligative properties of solutions, namely elevation of boiling point and depression in freezing point due to addition of solute. Elevation of Boiling Point: Boiling Point of a Liquid: Boiling point is […]