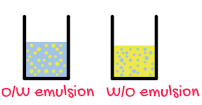
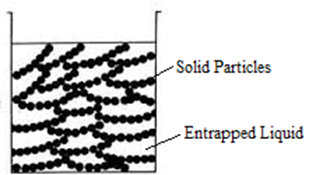
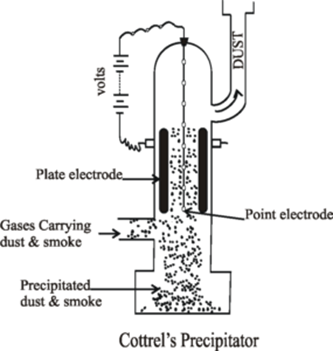
Science > Chemistry > Colloids > Applications of Colloids Natural Applications of Colloids: Blue Colour of Sky: When the light is incident on particles whose size is smaller than the wavelength of light, it is scattered. The blue colour of the sky is due to the scattering of light by small particles (dust particles along […]
Categories
Applications of Colloids
- Post author By Hemant More
- Post date April 20, 2020
- No Comments on Applications of Colloids
- Tags Alloys, Anionic surfuctants, Associated colloids, Cationic surfactants, Chemistry, Colloidal dispersions, Colloidal solution, Colloidal state, Colloids, Colour of sky, Crystalloids, Dispersed phase, Dispersion medium, Emulsion, Foam, Fog, Gas in liquid solutions, Gas in solid solution, Gels, Ink, Liquid aerosols, Liquid in gas solutions, Liquid in liquid solutions, Liquid in solid solutions, Lyophilic sols, Lyophobic sols, Macromolecular colloids, MIcelles, Mist, Multimolecular colloids, Non-ionic surfactants, Paints, Rain, Sewage precipitation, Smoke precipitation, Solid aerosols, Solid foam, Solid in gas solutions, Solid in liquid solutions, Solid in solid solutions, Solid sols, Sols, Solution, Surfactants, Suspension, True solution