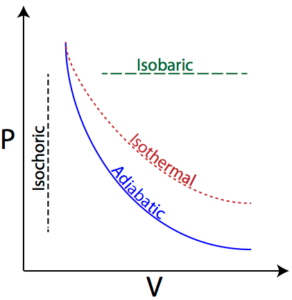
Science > Chemistry > Chemical Thermodynamics and Energetics > Concept of Maximum Work According to the first law of thermodynamics, ΔU = q + W In an isothermal process, ΔU = 0, ∴ q = – W Therefore, all the heat absorbed by the system is utilized to do work. […]
Categories
Concept of Maximum Work
- Post author By Hemant More
- Post date January 17, 2020
- 3 Comments on Concept of Maximum Work
- Tags Adiabatic process, Chemistry, Compression of gas, Constant pressure process, Constant temperature process, Constant volume process, Cyclic process, Expansion of gas, Free expansion, Irreversible process, Isobaric process, Isochoric process, Isothermal process, Isothermal reversible process, Maximum work, Pressure volume work, Process, Reversible process, Sign convention, work done in cyclic process