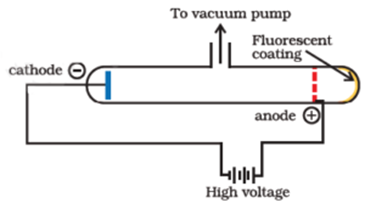
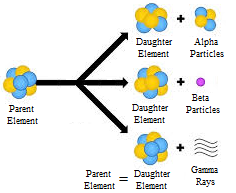
Science > Physics > Nuclear Physics > Discovery of Proton and Neutron Before the discovery of the atomic nucleus, there were ideas that all atoms are composed of hydrogen atoms (called by William Prout “protyles”). This hypothesis is known as Prout’s hypothesis. According to this hypothesis, the hydrogen atom was the only truly fundamental particles, […]
Categories
Discovery of Proton and Neutron
- Post author By Hemant More
- Post date May 8, 2020
- 2 Comments on Discovery of Proton and Neutron
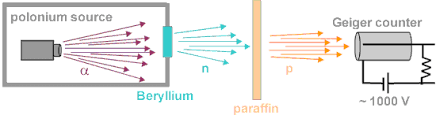
- Tags Alpha decay, Alpha particles, Beta decay, Beta particles, canal rays, Chadwick's experiment, Constituents of nucleus, Discovery of neutron, Discovery of proton, Gamma decay, gamma radiations, gamma rays, Natural radioactivity, Nuclear structure, Proton electron hypothesis, Proton neutron hypothesis, Radioactive decay, Radioactivity, Rutherford's experiment, Rutherford's model of an atom, Size of nucleus