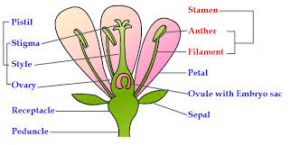
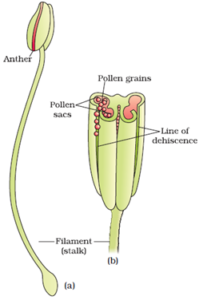
Science > Biology > Botany > Reproduction in Plants > Androecium and Gynoecium The flower is the reproductive unit in the angiosperms. It is meant for sexual reproduction. A typical flower has four different kinds of whorls arranged successively on the stalk or pedicel, called thalamus or receptacle. These whorls are calyx, corolla, androecium and […]
Categories
Androecium and Gynoecium
- Post author By Hemant More
- Post date April 5, 2020
- 1 Comment on Androecium and Gynoecium
- Tags Abiotic agents of pollination, Androecium, Anemophily, Apomixis, Asexual reproduction in plants, Biology, Biotic agents of pollination, Botany, Cellular endosperm, Ceratophyllum desnersum, Chiropterophily, Cross-pollination, Development of embryo, Development of endosperm, Development of Female Gamete, Development of Male gametophyte, Double fertilization, Endosperm, Entomophily, Epihydrophily, Fertilization, Formation of fruit, Formation of seed, Gynoecium, Helobial Endosperm, Hydrophilly, Hypohydrophily, Microsporangium, Nuclear endosperm, Ornithophily, Parthenocarpy, Pollen-Pistil Interaction, Pollination, Polyembyyony, Self-pollination, Sexual reproduction in moss, Sexual reproduction in plants, Sexual reproduction in spirogyra, Stigma, Structure of anther, Structure of ovule, Structure of pollen grain, Structure of seed, Zostera marina