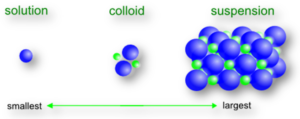
Science > Chemistry > Colloids >Types of Colloidal Solutions In this article, we shall study types of colloidal solutions (systems) on the basis of states of the dispersed phase and dispersion medium, the interaction between the dispersed phase and dispersion medium, and on the number of atoms and molecules in a colloidal particle. Types of […]
Categories
Types of Colloidal Solutions
- Post author By Hemant More
- Post date April 3, 2020
- 1 Comment on Types of Colloidal Solutions
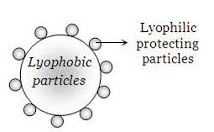
- Tags Alloys, Associated colloids, Chemistry, Colloidal dispersions, Colloidal solution, Colloidal state, Colloids, Crystalloids, Dispersed phase, Dispersion medium, Emulsion, Foam, Gas in liquid solutions, Gas in solid solution, Gels, Liquid aerosols, Liquid in gas solutions, Liquid in liquid solutions, Liquid in solid solutions, Lyophilic sols, Lyophobic sols, Macromolecular colloids, Multimolecular colloids, Solid aerosols, Solid foam, Solid in gas solutions, Solid in liquid solutions, Solid in solid solutions, Solid sols, Sols, Solution, Suspension, True solution