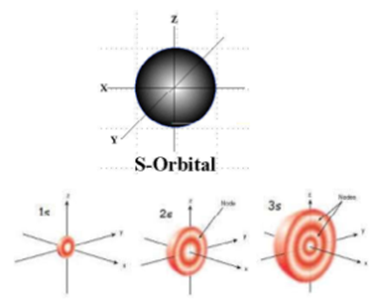
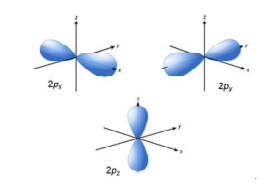
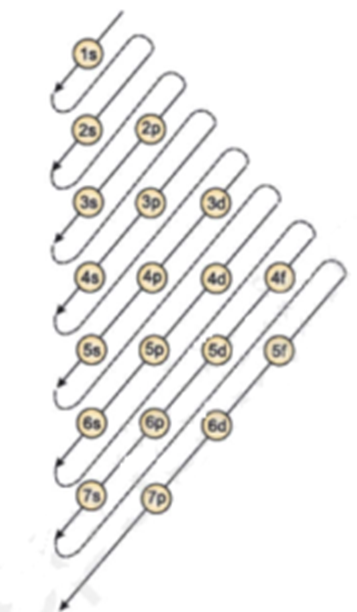
Science > Chemistry > Atomic Structure > Dual Nature of Radiations Light and other electromagnetic radiations have dual nature viz: the particle nature and the wave nature. Wave Nature of Radiations: Radiation is the form of energy, which can be transferred from one point to another point in space. Radiations are considered to be transmitted by wave […]
Categories
Dual Nature of Radiations
- Post author By Hemant More
- Post date July 31, 2020
- No Comments on Dual Nature of Radiations