Science > Chemistry > Introduction to Chemistry > Methods of Separation of Mixtures In the last article, we have studied the chemical classification of substances. Most of the available substances in nature are in mixture form. The useful component of the mixture can be obtained by separating individual components of the mixture by a suitable […]
Categories
Methods of Separation of Mixtures
- Post author By Hemant More
- Post date May 15, 2020
- 2 Comments on Methods of Separation of Mixtures
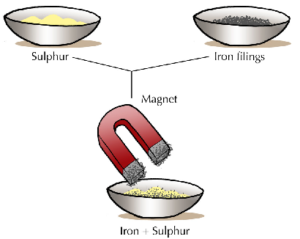
- Tags Centrifuging, Chemistry, Chromatography, Crystallization, Decantation, Diffusion, Distillation, Evaporation, Filteration, Fractional crystallization, Fractional distillation, Fractional evaporation, Gravity separation, Heating, Magnetic separation, Mechanical picking, Mixtures, Preferential liquefication, Sedimentation, Separation funnel, Separation of mixtures, Solvent extraction, Sublimation

